Introduction
There are several sources of law that are used to create and govern a legal system. These sources can vary depending on the jurisdiction, but some common sources of law include:
- Constitutions: A constitution is a document that establishes the fundamental principles and laws of a government. It often outlines the powers and duties of the different branches of government and the rights of the citizens.
- Statutes: Statutes are laws that are enacted by a legislative body, such as a parliament or congress.
- Administrative regulations: Administrative regulations are rules and orders issued by executive agencies to implement and enforce laws.
- Case law: Case law, also known as common law, is the body of law developed by the courts through the decisions of individual cases. It consists of judicial opinions, which interpret and apply the law to the facts of a particular case.
- Custom: Custom is the unwritten law that is created and followed by a community over time.
- International law: International law is the law that governs the relations between nations and other international entities. It can be found in treaties, conventions, and customary international law.
- Religious law: Religious law is the law that is based on the teachings of a particular religion and is followed by its believers.
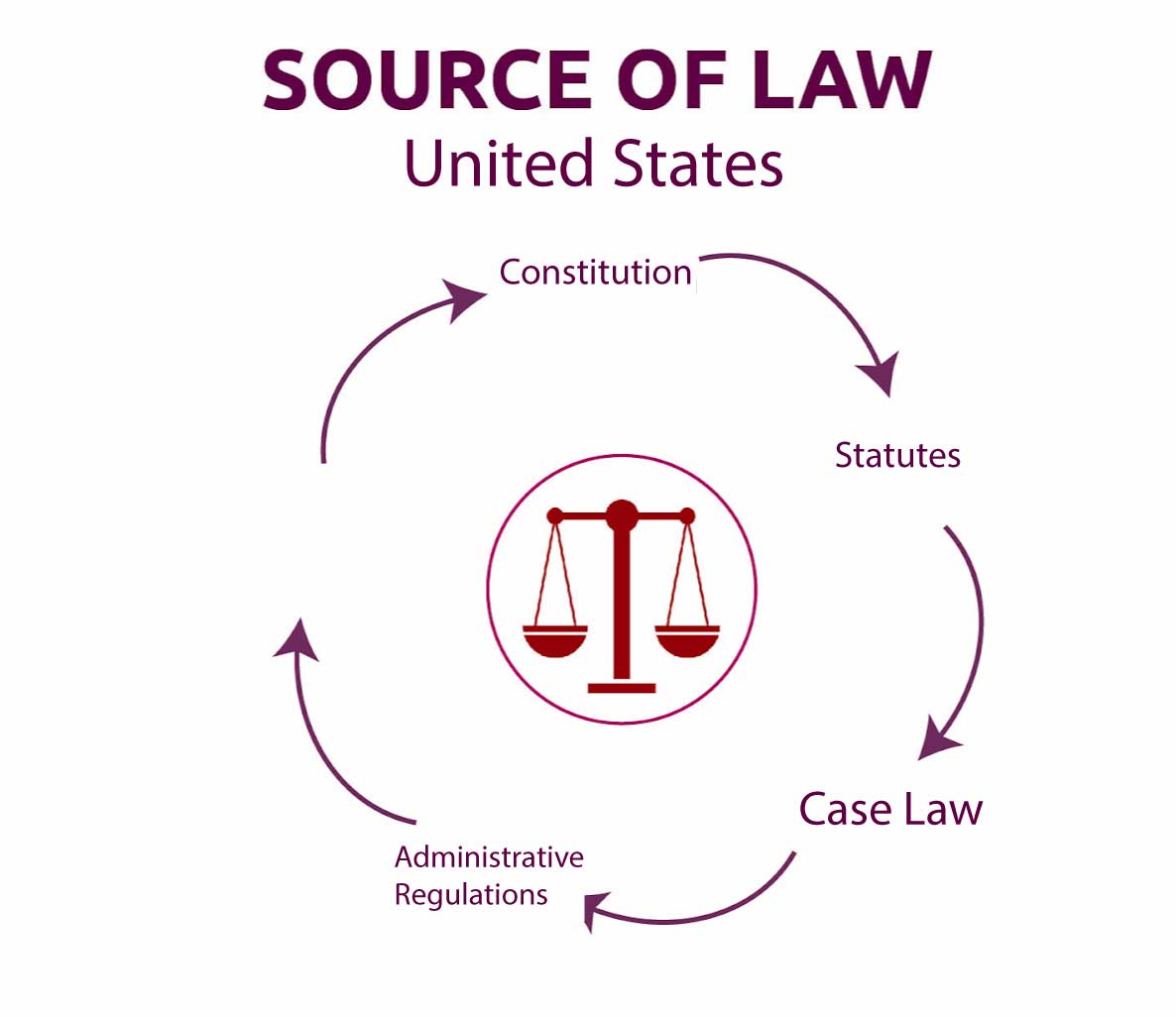
Sources of Law in the United States
In the United States, there are four main sources of law: the United States Constitution, federal and state statutes, administrative regulations, and case law.
- The Constitution
- Statutes
- Administrative regulations
- Case law or Judicial Decision
Constitution as a Source of Law in the United States
The United States Constitution is the supreme law of the land and is the primary source of law in the United States. It was adopted on September 17, 1787, by the Constitutional Convention in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, and took effect on March 4, 1789. The Constitution has a preamble and seven articles that delineate the national frame of government.
Article I, Section 1 of the Constitution establishes the legislative branch, which is responsible for making the laws. Article II, Section 1 establishes the executive branch, which is responsible for enforcing the laws. Article III, Section 1 establishes the judicial branch, which is responsible for interpreting the laws and applying them to the cases before the courts.
The Constitution also contains the Bill of Rights, which consists of the first ten amendments to the Constitution. These amendments protect the individual rights of American citizens, including freedom of speech, religion, and the press; the right to bear arms; the right to be free from unreasonable searches and seizures; and the right to a fair and speedy trial.
The Constitution is a flexible document that has been amended 27 times. It is interpreted by the courts, and their decisions help to define its meaning and application. The Constitution is the highest legal authority in the United States and is the foundation for the country’s legal system.
Statutes as a source of law in the United States
In the United States, statutes are a source of law that is created by the legislative branch of government. The legislative branch is responsible for making the laws, and it consists of Congress at the federal level and state legislatures at the state level.
Federal statutes are laws that are enacted by Congress, which is made up of the Senate and the House of Representatives. Congress has the power to make laws on a wide range of subjects, including taxation, trade, defense, and immigration.
State statutes are laws that are enacted by state legislatures, which are made up of elected representatives. State legislatures have the power to make laws on a variety of subjects, including education, health care, and criminal justice.
Statutes are usually written down and organized in a code, which is a collection of all the laws on a particular subject. For example, the United States Code is a collection of all the federal laws, and each state has its own code that contains the laws of that state.
Statutes are an important source of law because they provide a clear and concise expression of the law on a particular subject. They are typically more specific than the Constitution and provide more detail on how the law is to be applied.
Administrative Regulations as a Source of Law in the United States
In the United States, administrative regulations are a source of law that is created by executive agencies to implement and enforce the laws that are passed by Congress and state legislatures. Executive agencies are responsible for carrying out the laws and have the authority to make rules and regulations to do so.
Administrative regulations are created through a process known as rulemaking. During the rulemaking process, an executive agency will propose a new rule or regulation, and then solicit public comments on the proposed rule. After considering the comments, the agency will issue a final rule, which has the force of law.
Administrative regulations have the same authority as statutes and are often used to fill in the details of a law or to provide guidance on how to comply with a law. They can be found in the Code of Federal Regulations (CFR) at the federal level and in the state administrative codes at the state level.
Administrative regulations are an important source of law because they allow executive agencies to adapt to changing circumstances and to provide more specific guidance on how to comply with the law. However, they can also be controversial because they are created by executive agencies, which are not directly accountable to the public through the democratic process.
Case Law as a Source of Law in the United States
Case law, also known as common law, is a source of law in the United States that consists of judicial opinions, which interpret and apply the law to the facts of a particular case. It is created by the courts through the decisions of individual cases and is based on precedent, which is the principle that similar cases should be decided in a similar manner.
The United States has a common law system, which means that the law is not only found in written statutes, but also in the decisions of the courts. When a court decides a case, it will interpret the law and apply it to the facts of the case. The court’s decision, which is known as a judicial opinion, will become part of the case law on that subject.
Case law is an important source of law because it helps to interpret and apply the law to specific situations. It is also a source of flexibility because it allows the law to evolve and adapt to changing circumstances.
Case law is binding on lower courts within the same jurisdiction, but it is not necessarily binding on higher courts or courts in other jurisdictions. However, higher courts and courts in other jurisdictions will often consider the reasoning and analysis in a case when deciding similar cases. This is known as stare decisis, which is the principle that courts should follow precedent in similar cases.
- What is Mens Rea and Actus Reus - February 13, 2024
- Case Summary of Anglo Norwegian Fisheries Case | United Kingdom V Norway - April 7, 2023
- What is a Solicitor? How to Become One - January 9, 2023